Is sugar addictive? This question sparks a lively debate among health experts and nutritionists alike. While many people experience intense sugar cravings and compulsive eating behaviors akin to addiction, sugar itself is not classified as an addictive substance in the same way that alcohol or nicotine is. The health effects of sugar consumption, especially from processed foods laden with added sugars, can lead to habitual cravings and a cycle of overindulgence. Understanding the nuances of sugar addiction is crucial, as it influences how we manage our diets and the impact of added sugar consumption on our health.
The question of whether sugar possesses addictive properties is more nuanced than it might initially appear. Many people grapple with insatiable cravings for sweet treats and find it difficult to moderate their intake of foods rich in added sugar. This phenomenon is closely tied to our dietary habits, particularly as processed foods dominate the modern food landscape. Instead of viewing sugar purely as a dietary element, we can consider it through the lens of behavioral health, linking sugar addiction to compulsive eating habits and the overarching health implications of excessive sugar consumption.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
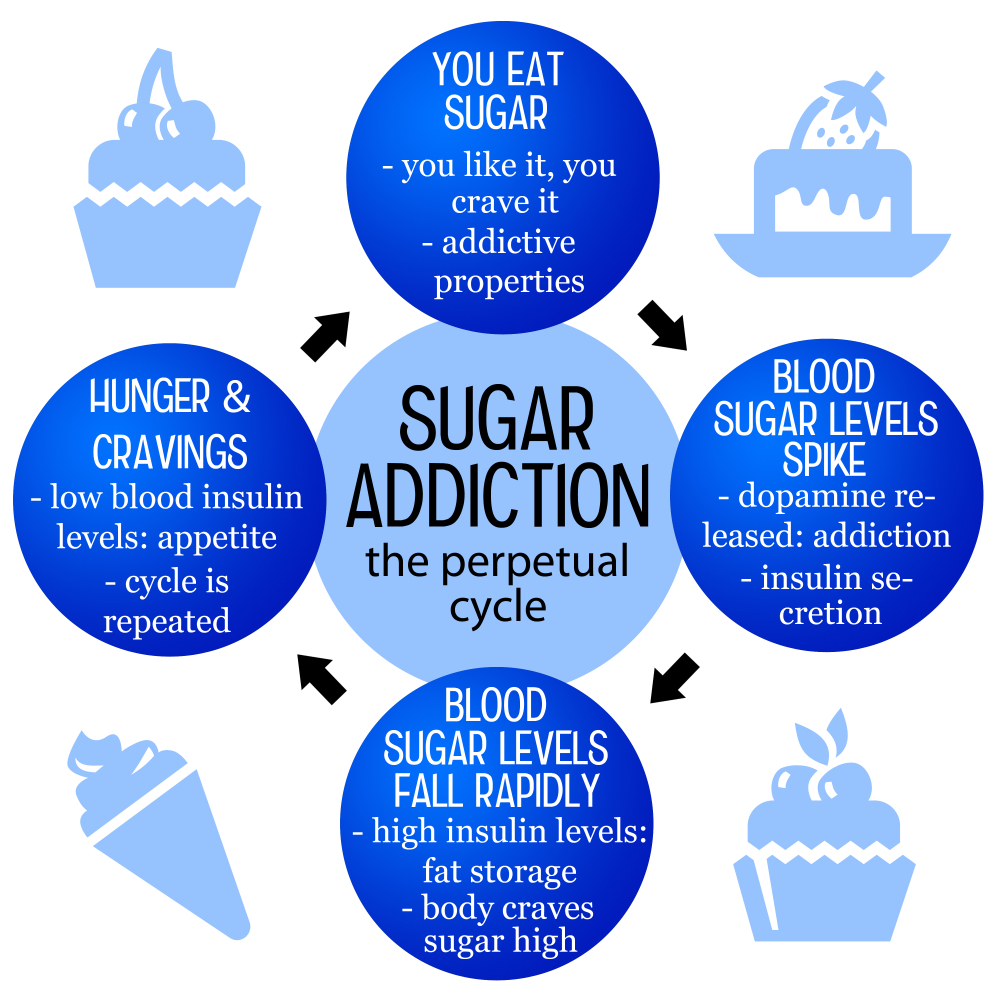
The question of whether sugar is addictive has sparked significant debate among nutritionists and health experts. While substances like alcohol and nicotine meet strict clinical criteria for addiction, sugar’s impact on cravings and eating behavior can mirror that of these addictive substances. Evidence suggests that sugar stimulates the brain’s reward system, leading to increased cravings and a tendency toward compulsive eating. However, it is essential to specify that while sugar can create a desire for more, it does not meet the same clinical definition of addiction as substances that can be fully eschewed from the diet.
Moreover, our modern diet, heavily populated with processed foods laden with added sugars, contributes to the normalization of high sugar consumption. This leads to a cycle of cravings, heightened by the palatability of sweet, high-calorie foods, which can create withdrawal-like symptoms upon reduction. But unlike alcohol or drugs, which can be completely eliminated, sugar is found naturally in many essential foods, such as fruits and vegetables. Thus, while we can recognize some addictive qualities in sugar, it’s essential to consider it in moderation rather than equating it directly with substances like nicotine or opiates.
Health Effects of Excess Sugar Consumption
The health implications of excessive sugar consumption cannot be overstated. The average American consumes nearly 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, far exceeding the recommendations from health organizations like the American Heart Association, which advises a limit of 9 teaspoons for men and 6 for women. This high intake has been associated with numerous health issues, including obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. The sheer volume of added sugar found in everyday foods, from beverages to snacks, amplifies the need for awareness about what we consume. Monitoring food labels can be a proactive step in addressing this health concern.
Moreover, the negative health consequences of sugar extend beyond physical ailments. Psychological effects such as anxiety and mood swings can occur, particularly when individuals drastically reduce their sugar intake after habitual consumption. This underscores the importance of approaching sugar reduction gradually, rather than going cold turkey, which could lead to unpleasant withdrawal symptoms. By understanding the health effects of sugar and choosing to limit processed foods high in added sugars, individuals can improve both their physical health and emotional well-being.
The Link Between Processed Foods and Sugar Cravings
Processed foods are often the largest culprits in the phenomenon of sugar cravings. These foods not only contain high amounts of added sugars but are also engineered to be hyper-palatable, making them difficult to resist. The convenience and taste of these products lead to habitual consumption that can perpetuate cravings. As these processed foods become staples in our diets, our taste preferences can shift, resulting in decreased satisfaction from healthier, less sugary options. This cycle can make it increasingly challenging for individuals to break free from cravings triggered by sugary snacks and drinks.
Addressing the cravings brought on by processed foods requires deliberate dietary choices. Incorporating whole foods—fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins—into daily meals can help manage cravings by providing the body with essential nutrients and fiber. These foods not only fill you up more effectively but also help to stabilize blood sugar levels, which can mitigate cravings for sweets. It’s essential to transition away from heavily processed items gradually, replacing them with nutritious alternatives that satisfy both hunger and taste without the significant sugar load.
Strategies to Manage Sugar Cravings
Managing sugar cravings involves a combination of awareness, dietary adjustments, and psychological strategies. One practical approach is to gradually decrease sugar intake instead of an abrupt elimination. This can help reduce withdrawal symptoms such as headaches, irritability, and mood swings that often accompany sudden dietary changes. Additionally, being mindful of food choices—like opting for snacks rich in protein and fiber—can diminish cravings, as they help maintain stable energy levels and satisfaction between meals.
Another effective method to manage cravings is to cultivate healthier behaviors and eating habits. For instance, staying hydrated, getting sufficient sleep, and engaging in regular physical activity can positively influence how your body manages sugar. Cognitive techniques, such as mindful eating, can also play a role in understanding your craving triggers and addressing them constructively. By being mindful of when and why you crave sugar, you can better equip yourself to make healthier choices that do not compromise your enjoyment of food.
The Importance of Educating Yourself on Added Sugar
Education regarding the types of sugars present in various foods is vital for making informed dietary choices. Many people overlook the hidden sugars in processed foods, which often carry labels that may not clearly indicate their sugar content. Familiarity with terms like ‘sucrose’, ‘fructose’, and ‘high-fructose corn syrup’, can empower consumers to recognize added sugars and their high-calorie implications. Learning to read and interpret nutrition labels correctly equips individuals to minimize their added sugar consumption and enhances overall health awareness.
Furthermore, understanding the connection between sugar consumption and health can motivate individuals to make better lifestyle choices. A well-informed public is better prepared to understand the broader implications of sugar intake—not only in terms of personal health but also within the context of public health initiatives aimed at combating the obesity epidemic. By educating ourselves and others on the implications of added sugar, we can foster a culture of health that values nutrition and well-being.
The Role of Sugar in a Balanced Diet
Sugar, while often demonized, can play a role in a balanced diet when consumed in moderation. It is important to differentiate between naturally occurring sugars in whole foods and the added sugars found in processed products. Natural sugars, such as those in fruits and dairy, provide essential nutrients along with sweetness, which can contribute to a healthy diet. In contrast, the excessive intake of added sugars from processed foods can lead to negative health consequences.
Incorporating sugar mindfully into your diet can enhance enjoyment without compromising health. Rather than eliminating sugar altogether, learning to savor less sugary desserts or beverages can allow for an enjoyable eating experience. By focusing on quality over quantity—choosing high-quality, minimally processed sugar sources—individuals can satisfy their sweet cravings without derailing their health goals.
Coping Mechanisms for Sugar Withdrawal Symptoms
When individuals decide to reduce their sugar intake, they may experience withdrawal symptoms similar to those seen with other addictive substances. Symptoms such as irritability, fatigue, and cravings can make it challenging to stick to a new eating plan. Developing coping mechanisms is crucial for those undergoing such a transition. Staying hydrated and ensuring adequate nutrition—especially fiber and protein—can help stabilize blood sugar levels and mitigate some of these withdrawal effects.
Additionally, engaging in physical activities can serve as a powerful distraction and mood enhancer during the beginning stages of reducing sugar intake. Activities such as walking, cycling, or dancing release endorphins, which not only uplift spirits but can also help alleviate cravings. Combining physical activity with mindfulness practices, such as meditation or yoga, can foster a greater sense of control over one’s food choices and enhance overall well-being.
Finding Support in Sugar Reduction Efforts
Embarking on a journey to reduce added sugar intake can be daunting, but finding support can significantly increase the chances of success. Connecting with like-minded individuals through support groups, online forums, or community programs can provide encouragement and share practical tips. These platforms offer valuable experiences and strategies from those who understand the challenges and successes involved with reducing sugar.
Additionally, seeking guidance from health professionals, such as registered dietitians or nutritionists, can provide personalized advice tailored to individual health goals. Professional support can help set realistic expectations, offer meal planning strategies, and provide ongoing motivation to adhere to sugar reduction efforts. Overall, finding community and expert support can enhance the journey of managing sugar cravings effectively.
Concluding Thoughts on Sugar Consumption
While the question of whether sugar is addictive is complex, it is undeniable that managing sugar consumption is essential for maintaining health. Balancing the enjoyment of sweet flavors with health-conscious choices can create a sustainable approach to eating. Understanding one’s relationship with sugar, recognizing cravings for what they are, and making informed dietary choices can lead to healthier habits.
In sum, reducing added sugar intake does not have to mean deprivation. Instead, it should be the beginning of a mindful relationship with food that prioritizes health, enjoyment, and balance. By focusing on gradual changes, education, and support, individuals can transition toward a diet that is both satisfying and supportive of their overall health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like alcohol or nicotine?
While sugar can increase cravings and lead to compulsive eating behaviors, it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. The psychological and physical cravings for sugar are real, especially due to the prevalence of highly processed foods containing added sugars, but they are typically less intense than withdrawal symptoms from true addictive substances.
What are the health effects of sugar addiction?
Sugar addiction can lead to various health effects, including increased cravings, habitual consumption of sugary foods, and potential weight gain. Research suggests that consuming high amounts of added sugar, prevalent in processed foods, can also contribute to conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease.
How do sugar cravings relate to processed foods?
Sugar cravings are often intensified by the consumption of processed foods that contain high levels of added sugars. These foods are designed to be highly palatable and accessible, making it easier to develop a habitual consumption pattern that can trigger cravings and feelings of dependence on sugar.
Can cutting out sugar lead to withdrawal symptoms?
Yes, abruptly cutting out sugar can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, and anxiety. This is particularly true for individuals who consume high amounts of added sugars regularly. Gradually reducing sugar intake may help mitigate these withdrawal effects.
What is the recommended limit for added sugar consumption?
The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar consumption to no more than 9 teaspoons per day for men, 6 teaspoons for women, and much less for children. Being mindful of added sugars in your diet is crucial for maintaining health and preventing the adverse effects of excessive sugar intake.
Is it possible to live without sugar?
While it is possible to eliminate added sugars from your diet, complete avoidance of all sugars is impractical since they occur naturally in many healthy foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. Instead, it is important to focus on moderating added sugar intake for optimal health.
How can I reduce my sugar consumption effectively?
To reduce sugar consumption effectively, start by reading food labels to understand the sugar content in processed foods. Gradually decrease your intake of sugary snacks and beverages instead of quitting cold turkey, which can lead to increased cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
Are there benefits to consuming sugar in moderation?
Yes, consuming sugar in moderation can enhance the flavor of foods and improve texture without significantly impacting health. It is essential to balance sugar intake within the context of a healthy diet that includes whole foods, while being aware of the potential for cravings and overconsumption.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Is Sugar Addictive? | Debated topic; not classified as addictive by clinical criteria. |
| Cravings and Withdrawal Symptoms | Sugar can cause cravings and eating behaviors similar to addiction, but withdrawal symptoms are less severe than with substances like alcohol and nicotine. |
| Importance of Sugar in Diet | Sugar is present in healthy foods; moderation is key. |
| Recommended Sugar Intake | American Heart Association recommends no more than 6-9 teaspoons of added sugar daily, depending on age and gender. |
| Reading Labels and Gradual Reduction | Awareness of sugar content in foods is essential; reducing added sugar should be gradual, not abrupt. |
| Conclusion | While sugar exhibits some addictive qualities, it is fundamentally different than addictive substances such as nicotine, with appropriate levels enhancing flavor and pleasure in our diets. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? The topic of sugar addiction is complex and often debated among health experts. While cravings for sugary foods can resemble those seen in addiction to substances like alcohol and nicotine, sugar is not classified as an addictive substance by current clinical standards. This distinction is important as it highlights that, while sugar can lead to habitual consumption and mild withdrawal-like symptoms upon cessation, it provides essential energy in our diets and is naturally found in many healthy foods. Thus, moderation is key, and understanding sugar’s role in nutrition can help maintain a balanced diet.