Alzheimer’s early detection is becoming increasingly vital as researchers uncover innovative methods to identify the risk of this devastating condition before symptoms manifest. A groundbreaking home test developed at Mass General Brigham relies on olfactory testing—allowing individuals to sniff odor labels and evaluate their scent discrimination abilities. This simple yet effective Alzheimer’s disease test can bring clarity to the often murky waters of cognitive impairment, allowing for timely interventions. Early identification of neurodegenerative disease detection is not only transformative for patients but also crucial for advancing treatment strategies. As we delve deeper into the importance of cognitive health, understanding the links between smell and Alzheimer’s presents a promising avenue for future research.
The pursuit of identifying early warning signs of cognitive decline is gaining momentum, particularly through innovative assessments that target neurological health. Techniques such as smell tests, which evaluate the ability to perceive and differentiate scents, are emerging as essential tools in the realm of dementia screening. These assessments, often referred to as cognitive impairment tests, can predict the onset of Alzheimer’s well before overt symptoms arise. With options like a home test for Alzheimer’s now available, individuals can monitor their cognitive abilities with greater ease and accuracy. By embracing this proactive approach, we position ourselves to combat not just Alzheimer’s, but also associated neurodegenerative diseases, ushering in a new era of preventative care.
Understanding Alzheimer’s Early Detection Methods
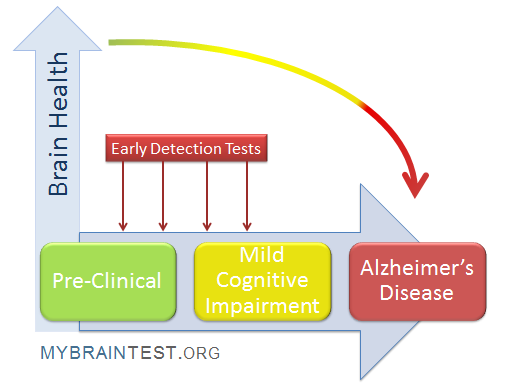
The quest for early detection methods for Alzheimer’s disease has been a priority in medical research, especially as the aging population increases. Innovative tests have emerged, including cognitive impairment tests and olfactory assessments, which are particularly promising. Early detection is critical as it enables timely interventions that may halt or slow progression, allowing those at risk to take proactive measures regarding their health and lifestyle. By focusing on biomarkers that can be discerned long before memory symptoms emerge, these tests provide hope for improving outcomes for individuals with neurodegenerative diseases.
Among the recent advancements is a home test for Alzheimer’s that incorporates olfactory testing, where participants engage their sense of smell to identify different odors. Research indicates that individuals suffering from cognitive impairment demonstrate notable deficiencies in olfactory functioning compared to their cognitively intact counterparts. Thus, utilizing these non-invasive methods not only empowers patients by allowing them to test themselves at home but also enhances accessibility to early detection strategies, encouraging more people to seek intervention at just the right moment.
The Role of Olfactory Testing in Detecting Cognitive Impairments
Olfactory testing has surfaced as a groundbreaking approach in the field of Alzheimer’s disease detection due to its simplicity and the increasing evidence linking diminished smell perception to cognitive decline. Researchers have successfully shown that the ability to process and identify scents decreases in individuals with Alzheimer’s, making it a valuable indicator for cognitive impairment. This method not only facilitates at-home testing but also serves as a cost-effective alternative to traditional cognitive assessments, which can often be complex and invasive.
Moreover, olfactory testing can be particularly advantageous in multilingual contexts, allowing researchers to engage diverse populations, as demonstrated in recent studies involving English and Spanish speakers. This inclusivity expands the reach of cognitive health assessments and ensures that interventions can be designed for a broader demographic. Implementing such tests in clinical settings could greatly enhance our understanding of cognitive decline patterns, ultimately aiding in the development of tailored treatment chronologies for neurodegenerative diseases.
Importance of Cognitive Impairment Tests in Alzheimer’s Research
Cognitive impairment tests are essential tools in Alzheimer’s research, providing crucial data that can lead to earlier and more accurate diagnoses. These tests not only assess memory and reasoning skills but can also be integrated with olfactory testing to create a comprehensive evaluation approach. They allow researchers to track the progression of cognitive decline and identify those who may benefit from early interventions. Assessing cognitive performance in relation to sensory functioning provides insights into the complex interactions within the brain as it ages.
Furthermore, utilizing a combination of cognitive and olfactory tests can refine the specificity of Alzheimer’s disease markers, significantly impacting treatment strategies and personal care plans. Providing a means to detect neurodegenerative diseases early ensures that patients and families can access resources and support as needed. As research continues to evolve, these combined tests will likely lead to greater understanding and management of Alzheimer’s, pioneering pathways for future scientific inquiries into the disease.
Utilizing Home Tests for Alzheimer’s Awareness and Prevention
The advent of home tests for Alzheimer’s, particularly through olfactory testing, is revolutionizing the way individuals approach cognitive health at an earlier age. Such innovation fosters a sense of empowerment among individuals who may be concerned about their cognitive health, encouraging them to take proactive steps towards monitoring their well-being. By shifting the responsibility of early detection to the individual, these home-based screening tools can lead to higher awareness and acceptance of potential health declines.
Moreover, accessibility to these non-invasive tests promotes a shift in the stigma surrounding cognitive decline. Families and caregivers can utilize these comprehensive tools to evaluate cognitive changes over time, making it easier to engage in discussions about Alzheimer’s and its implications. The early detection provided by these tests is crucial, as it lays the groundwork for timely medical consultations and lifestyle adjustments that can improve overall health outcomes for those facing neurodegenerative challenges.
Innovations in Alzheimer’s Testing: The Aromha Brain Health Test
The development of the Aromha Brain Health Test signals a significant milestone in the initiative to identify Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. This olfactory assessment has been validated through comprehensive studies and demonstrates an effective way to detect subtle changes in cognitive function linked to Alzheimer’s. The test utilizes the sense of smell, which, as evidence suggests, can predict cognitive impairments that go unnoticed in standard cognitive assessments.
Harnessing the innovative potential of this test, researchers have created a pathway for widespread application, especially beneficial for geriatric populations and non-English-speaking individuals. By fostering early detection, the Aromha Brain Health Test stands as a pivotal tool in combating Alzheimer’s, allowing for more timely interventions and care strategies that could enhance quality of life for individuals at risk. This represents a giant leap in integrating everyday health practices with advanced medical research.
Breaking Down the Research Behind Olfactory Dysfunction and Alzheimer’s
Research findings consistently indicate that olfactory dysfunction can serve as a significant early warning sign for Alzheimer’s disease. Studies show that older adults who struggle with odor identification often experience greater cognitive impairments compared to their peers. This relationship highlights the need for incorporating olfactory testing into regular health assessments, as it can provide insights that traditional cognitive tests might overlook, paving the way for a deeper understanding of Alzheimer’s pathology.
Moreover, ongoing studies are emphasizing the potential of olfactory testing to predict later stages of cognitive decline and inform research agendas aimed at developing effective treatment strategies. Researchers advocate for further examination of olfactory function as a biomarker for neurodegenerative diseases, noting its potential to revolutionize the landscape of Alzheimer’s research and treatment. This intersection of sensory science and cognitive health can not only validate early intervention measures but also inspire new therapeutic approaches.
Promoting Public Awareness About Alzheimer’s Disease Testing
Increasing public awareness about Alzheimer’s disease testing, specifically through methods like olfactory assessment, is essential for fostering a culture of proactive health engagement. Family members and caregivers play a crucial role in recognizing the signs of cognitive decline in loved ones, and by being informed about the various testing options available, they can support early screening initiatives. Public health campaigns emphasizing the importance of taking home tests for Alzheimer’s will empower individuals and communities to prioritize cognitive health.
Educating the public regarding the correlation between sensory loss, particularly the sense of smell, and Alzheimer’s disease can also demystify the testing process. Utilizing mixed media approaches, including informative seminars and digital engagement, can foster a better understanding of cognitive health issues. This proactive approach aims to break down barriers to early detection and intervention, potentially leading to improved quality of life for those facing the specter of Alzheimer’s.
Future Directions in Alzheimer’s Disease Detection Research
As research into Alzheimer’s disease detection continues to evolve, it is essential to examine novel methods and technologies that can enhance early identification of cognitive decline. The integration of olfactory testing into broader Alzheimer’s screening processes presents an exciting frontier, inviting researchers and healthcare professionals to explore synergies between sensory perception and cognitive health. Future studies must focus on honing methodologies to ensure accuracy and relevance for diverse demographics, aiming for inclusivity and accessibility.
Further investments in research will be necessary to support the advancement of at-home tests for Alzheimer’s disease, ensuring they are validated for various populations. As the demand for early detection grows, it is vital for the scientific community to remain committed to exploring innovative pathways that will improve the diagnostic landscape for neurodegenerative diseases. By embracing a holistic approach to Alzheimer’s research, we can uncover comprehensive risk profiles and facilitate timely interventions that pave the way for healthier aging.
The Impact of Cultural Context on Alzheimer’s Testing
Understanding the cultural implications of Alzheimer’s testing is an important aspect of ensuring accessibility and efficacy in neurodegenerative disease detection. Different communities may have varying perceptions of cognitive health, influenced by language, traditions, and health literacy. Therefore, integrating culture into the design and implementation of olfactory testing and other cognitive impairment tests is a critical step toward promoting widespread adoption.
By considering cultural nuances, researchers can create tailored outreach programs that resonate with diverse populations. This approach can improve not only participation rates in testing but also the comprehension and acceptance of the results. Ensuring that all individuals have the opportunity to engage in monitoring their cognitive health is paramount for advancing Alzheimer’s disease research and ensuring equitable healthcare access.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of olfactory testing in Alzheimer’s early detection?
Olfactory testing plays a crucial role in Alzheimer’s early detection by assessing an individual’s ability to identify and discriminate odors. Research shows that older adults with cognitive impairment often perform poorly on these tests. By identifying olfactory dysfunction early, healthcare providers can indicate a potential risk for Alzheimer’s disease and intervene before memory symptoms emerge.
How can I perform a home test for Alzheimer’s using olfactory methods?
To perform a home test for Alzheimer’s using olfactory methods, you can use simple odor identification cards or kits designed for this purpose. These tests involve sniffing different odor labels and determining which smells you can identify. If you notice difficulties in identifying or discriminating odors, it may warrant further evaluation for cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease.
What types of Alzheimer’s disease tests are available for early detection?
There are various Alzheimer’s disease tests available for early detection, including cognitive impairment tests, olfactory tests, and neuropsychological assessments. These tests help evaluate memory, reasoning, and sensory functions to identify individuals at risk for Alzheimer’s. Engaging in these tests can provide early signs of cognitive decline, allowing for timely interventions.
Can olfactory dysfunction indicate early signs of neurodegenerative disease such as Alzheimer’s?
Yes, olfactory dysfunction can indicate early signs of neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s. Studies have shown that a decline in the ability to smell can precede other cognitive symptoms. This correlation makes olfactory testing a valuable tool in the early detection of Alzheimer’s disease.
Are there any cost-effective Alzheimer’s early detection tests I can use at home?
Yes, there are cost-effective Alzheimer’s early detection tests available for home use. The Aromha Brain Health Test is one such example, utilizing olfactory testing to assess risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease. These non-invasive tests can be performed at home, providing valuable insights into cognitive health without the need for extensive clinical visits.
What role does cognitive impairment testing play in Alzheimer’s early detection?
Cognitive impairment testing is essential for Alzheimer’s early detection as it evaluates memory, problem-solving skills, and other cognitive functions. These tests help identify individuals with mild cognitive impairment, a condition that may lead to Alzheimer’s disease, allowing for early intervention and management strategies.
How can early detection of Alzheimer’s improve patient outcomes?
Early detection of Alzheimer’s can significantly improve patient outcomes by allowing for timely interventions, such as lifestyle changes, medication, and supportive therapies. Recognizing the disease in its initial stages can help manage symptoms effectively, plan for the future, and maintain a better quality of life for patients and their families.
What is the connection between olfactory testing and cognitive decline?
The connection between olfactory testing and cognitive decline lies in the observation that individuals with Alzheimer’s disease often exhibit reduced olfactory function. Scientific studies indicate that as cognitive decline progresses, the ability to identify and remember odors also diminishes, making olfactory tests a potential early indicator of cognitive impairment.
| Key Points | |
|---|---|
| Researchers at Mass General Brigham developed an at-home olfactory test for early Alzheimer’s detection. | The test assesses the ability to discriminate, identify, and remember various odors. |
| Older adults with cognitive impairment scored lower than those without issues. | The study suggests that olfactory dysfunction could serve as an early warning sign for Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases. |
| Participants reported cognitive complaints, leading to comparisons with cognitively normal individuals and those with no smell. | Results showed olfactory abilities decline with age and correlate with cognitive impairment. |
| The study indicates that olfactory testing could be useful for predicting cognitive decline across different languages. | Future studies may integrate neuropsychological tests to enhance early detection methods. |
Summary
Alzheimer’s early detection is crucial for effective intervention, as it can identify risks before memory symptoms begin. Recent advancements at Mass General Brigham have introduced an innovative at-home olfactory test that utilizes the sense of smell to assess cognitive health. This groundbreaking approach not only facilitates easy access for older adults but also highlights the potential for early intervention in neurodegenerative diseases, paving the way for future research and better treatment outcomes.